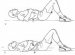
What Exercises is Good for back pain?
 GETTY
GETTY
Over-the-counter pills such as ibuprofen are rarely effective when it comes to relieving chronic back pain, scientists have discovered.
In a ground breaking new study, just one patient in six achieved any significant pain relief.
Doctors say concentrating on exercise programmes to boost our core muscles, therefore strengthening the back, is much more effective.
An estimated sixth of the UK population suffers from back pain at any one time, costing the economy up to £1billion a year.
Related articles
 Our results show anti-inflammatory drugs actually only provide very limited short-term pain relief
Our results show anti-inflammatory drugs actually only provide very limited short-term pain relief
Back, neck and muscle problems led to a staggering 31 million days of work being lost last year, according to the Office for National Statistics.
Associate Professor Manuela Ferreira, of the George Institute for Global Health in Australia, which carried out the new study, said: “Back pain is the leading cause of disability worldwide and is commonly managed by prescribing medicines such as anti-inflammatories.
“But our results show anti-inflammatory drugs actually only provide very limited short-term pain relief. They do reduce the level of pain, but only very slightly, and arguably not of any clinical significance.
“When you factor in the side effects which are very common, it becomes clear that these drugs are not the answer to providing pain relief to the many millions who suffer from this debilitating condition every year.”
GETTY
An estimated sixth of the UK population suffers from back pain at any one timePhysiotherapists welcomed the study’s findings, pointing out that exercise can often be the key to tackling the problem. Tim Hutchful, of the British Chiropractic Association, said: “I would agree with the research that prevention is always better than cure when it comes to back pain.